Adapted from Wikipedia
The guild was made up by experienced and confirmed experts in their field of handicraft. They were called master craftsmen. Before a new employee could rise to the level of mastery, he had to go through a schooling period during which he was first called an apprentice. After this period he could rise to the level of journeyman. Apprentices would typically not learn more than the most basic techniques until they were trusted by their peers to keep the guild’s or company’s secrets.
Like journey, the distance that could be traveled in a day, the title ‘journeyman’ derives from the French words for ‘day’ (jourand journée) from which came the middle English word journei. Journeymen were able to work for other masters, unlike apprentices, and generally paid by the day and were thus day laborers. After being employed by a master for several years, and after producing a qualifying piece of work, the apprentice was granted the rank of journeyman and was given documents (letters or certificates from his master and/or the guild itself) which certified him as a journeyman and entitled him to travel to other towns and countries to learn the art from other masters. These journeys could span large parts of Europe and were an unofficial way of communicating new methods and techniques, though by no means all journeymen made such travels — they were most common in Germany and Italy, and in other countries journeymen from small cities would often visit the capital.
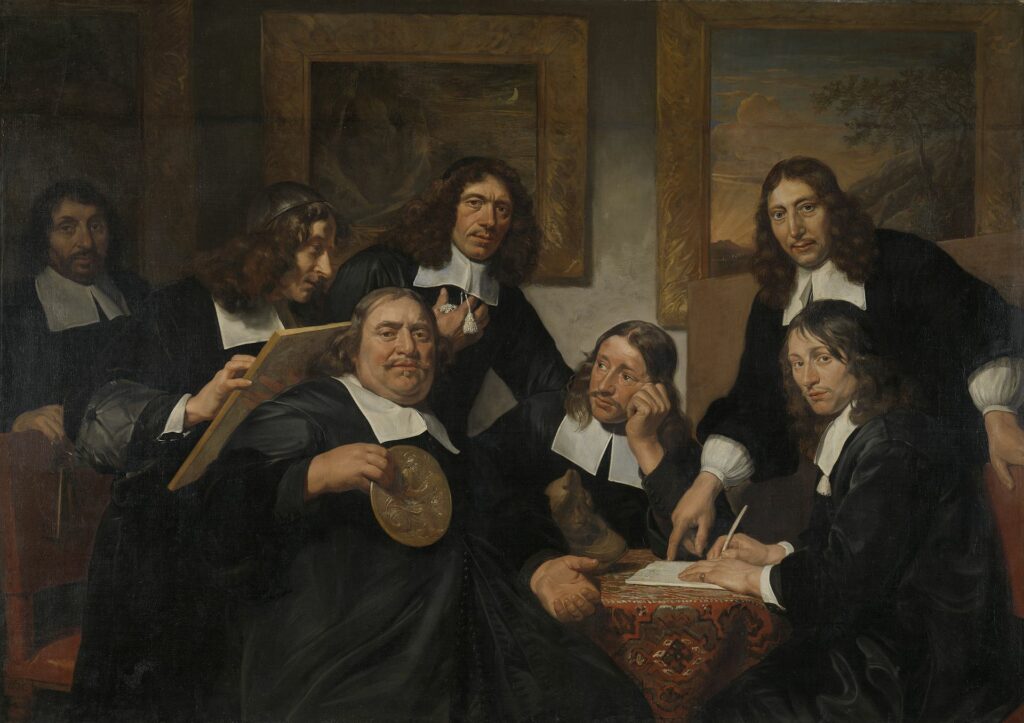

After this journey and several years of experience, a journeyman could be received as master craftsman, though in some guilds this step could be made straight from apprentice. This would typically require the approval of all masters of a guild, a donation of money and other goods (often omitted for sons of existing members), and the production of a so-called “masterpiece,’ which would illustrate the abilities of the aspiring master craftsman; this was often retained by the guild.